Natural supplements that prevent low mood after using psychedelic substances (ketamine, MDMA, LSD, Psilocybin)
Disclaimer: Many people come to our office looking to get off of their anti-depressant and/or anti-anxiety medications. They want to be off them and maybe take a natural supplement instead. If you are on a medication like this please DO NOT STOP THEM without the help of your psychiatrist and/or therapist!
It is very common to feel a bit down or even outright depressed after receiving a ketamine IV or using various psychedelic medications. Why is this? It has to do with the supply of neurotransmitters in the brain.
Why Do I Feel Down a Few Days After My Ketamine IV or After Using Various Psychedelic Drugs?
1. What are neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are chemicals in the brain that help to transmit signals between neurons (nerve cells) and other cells in the body. They are released from the end of one neuron, called the presynaptic cell, and bind to receptors on the next neuron, called the postsynaptic cell, in order to transmit the signal across the synapse (the gap between the two neurons).
Neurotransmitters play a vital role in a variety of functions in the brain, including:
- Regulating mood: Serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine are neurotransmitters that are involved in regulating mood and are often targeted by medications used to treat depression and anxiety.
- Controlling movement: Dopamine is also involved in controlling movement and is the primary neurotransmitter affected in Parkinson’s disease.
- Regulating appetite: Neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin are involved in regulating appetite and are thought to play a role in conditions such as obesity and eating disorders.
- Modulating pain: Endorphins and enkephalins are neurotransmitters that are involved in modulating pain perception.
- Regulating sleep: Neurotransmitters such as serotonin and norepinephrine are involved in regulating sleep and wakefulness.
- Forming memories: Neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine and glutamate are involved in forming memories and learning.
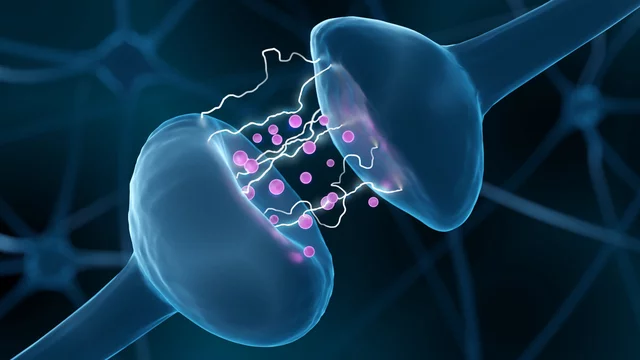
2. How do psychoactive substances affect the neurotransmitters?
Psychoactive drugs (MDMA, mushrooms, Ketamine, LSD) affects the brain’s neurotransmitter systems, particularly serotonin. While it produces euphoric and empathogenic effects, it can also deplete neurotransmitters and lead to a feeling of low mood, often referred to as the “comedown” or “crash.”
“Empathogenic” drugs: Empathogens or entactogens are a class of psychoactive drugs that produce experiences of emotional communion, oneness, relatedness, emotional openness—that is, empathy or sympathy.
Here’s a description of the process (using MDMA as an example):
- Serotonin Release: MDMA primarily acts by increasing the release of serotonin, a neurotransmitter responsible for regulating mood, emotions, and other functions. It causes serotonin to flood the synapses, leading to increased feelings of happiness, empathy, and well-being.
- Neurotransmitter Depletion: MDMA use can result in the depletion of serotonin in the brain. When large amounts of serotonin are released, the storage sites within the neurons become emptied, and the natural supply of serotonin becomes depleted. This depletion occurs because MDMA affects the mechanisms responsible for storing and reabsorbing serotonin.
- Altered Serotonin Levels: After MDMA use, the brain’s serotonin levels are temporarily reduced. This sudden drop in serotonin can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters, affecting mood, sleep, appetite, and other emotional and cognitive functions. The depleted levels of serotonin contribute to the “low mood” or feelings of depression that can follow MDMA use.
- Neurotransmitter Replenishment: The brain needs time to replenish its serotonin levels after MDMA use. It typically takes time for the brain to regenerate and restore the depleted neurotransmitters to their normal levels. During this period, individuals may experience a temporary state of low mood, sadness, or even depression.
It’s important to note that the extent of neurotransmitter depletion and the severity of the comedown can vary from person to person, depending on factors such as dosage, frequency of use, individual physiology, and other contextual factors.
To support recovery and minimize the negative effects of MDMA use, individuals are advised to practice harm reduction techniques, such as:
- avoiding excessive doses
- taking breaks between uses to allow the brain to recover
- staying hydrated
- getting adequate rest and nutrition
- It is also crucial to seek professional help if experiencing persistent or severe depressive symptoms after MDMA use.
3. How to prevent the “crash” after using psychedelic drugs?
To really support brain recovery after using drugs like this is is important to provide your body with the ingredients to build more neurotransmitters.
Here is a list of key supplements to take to prevent the “crash” after using empathogenic drugs:
1. 5-HTP: 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) is a naturally occurring amino acid and chemical precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and other cognitive functions. Here’s a description of what 5-HTP does:
- Serotonin Synthesis: 5-HTP is converted into serotonin in the brain. After ingestion, 5-HTP crosses the blood-brain barrier and enters the central nervous system. Inside the brain, it is enzymatically converted into serotonin by an enzyme called aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase.
- Serotonin Regulation: Once converted, serotonin acts as a neurotransmitter, transmitting signals between nerve cells. It helps regulate mood, emotions, appetite, pain perception, sleep-wake cycles, and various other physiological and cognitive processes.
- Appetite Control: Serotonin is involved in appetite regulation, and low serotonin levels are associated with increased food cravings and overeating. By boosting serotonin production, 5-HTP may help suppress appetite, reduce carbohydrate cravings, and promote a feeling of fullness, which can aid in weight management and control emotional eating.
- Pain Management: Serotonin is involved in the modulation of pain signals in the central nervous system. Increasing serotonin levels through 5-HTP supplementation may help alleviate certain types of pain, such as headaches, migraines, and fibromyalgia. However, further research is needed to fully understand its effectiveness in pain management.
- Management of Serotonin-related Conditions: Some conditions are associated with low serotonin levels, such as fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, and premenstrual syndrome (PMS). 5-HTP supplementation has been studied for its potential benefits in managing these conditions. It may help reduce pain, fatigue, and improve other associated symptoms.
2. SAM-e: S-Adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM-e) is a compound that occurs naturally in the body and plays a vital role in various biochemical processes. It is involved in the synthesis, activation, and metabolism of several substances in the body, including neurotransmitters, hormones, and phospholipids. Here are some of the potential benefits associated with SAM-e supplementation:
- Mood Support: SAM-e has been extensively studied for its positive effects on mood disorders, particularly depression. It is believed to enhance the production and function of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which are involved in regulating mood. SAM-e supplementation has shown promise in reducing symptoms of depression and improving overall mood.
- Joint Health: SAM-e has been found to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help alleviate joint pain and improve mobility in individuals with conditions such as osteoarthritis. It is thought to support cartilage health by promoting the synthesis of proteoglycans, which are essential components of cartilage and joint fluid.
- Liver Health: The liver requires SAM-e for various metabolic processes, including detoxification and the production of glutathione, a potent antioxidant. Supplementing with SAM-e has shown potential in supporting liver function and protecting against liver damage caused by certain medications, toxins, or conditions like liver disease.
- Cognitive Function: SAM-e may have cognitive benefits, particularly in age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders. It is involved in the synthesis and metabolism of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter important for memory and cognitive function. Some studies suggest that SAM-e supplementation may improve cognitive performance, memory, and overall brain health.
- Fibromyalgia and Chronic Pain: SAM-e has been investigated for its potential in managing fibromyalgia and chronic pain conditions. It may help reduce pain intensity and improve physical functioning in individuals with these conditions. However, more research is needed to establish its effectiveness and optimal dosage for pain management.
3. Methylated B12: Methylated B12, also known as methylcobalamin, is a form of vitamin B12 that has been shown to have various benefits for mood and mental well-being. Here are some of the potential benefits of methylated B12 on mood:
- Enhanced Methylation: Methylcobalamin is the active and bioavailable form of vitamin B12, and it plays a crucial role in a process called methylation. Methylation is involved in numerous biochemical reactions in the body, including the production and regulation of neurotransmitters that affect mood. By supporting methylation processes, methylated B12 may help maintain optimal neurotransmitter function, which can contribute to improved mood and mental health.
- Increased Serotonin Production: Methylated B12 is involved in the synthesis of serotonin, a neurotransmitter known for its role in regulating mood. Adequate levels of serotonin are associated with a positive mood and feelings of well-being. By supporting serotonin production, methylated B12 may help alleviate symptoms of depression and promote a more stable and positive mood.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Methylated B12 has been found to have neuroprotective properties, helping to protect nerve cells and support their proper functioning. This is important because disruptions in neurological processes can contribute to mood disorders. By promoting the health and integrity of nerve cells, methylated B12 may help maintain optimal brain function and support overall mental well-being.
- Energy and Fatigue Reduction: Vitamin B12, including the methylated form, is essential for the production of red blood cells and the conversion of food into energy. Fatigue and low energy levels can significantly impact mood and overall mental health. By ensuring adequate energy production, methylated B12 may help reduce fatigue, increase energy levels, and improve overall vitality, which can positively influence mood.
- Cognitive Function Support: Methylated B12 is important for maintaining healthy cognitive function. It is involved in the production of myelin, a protective coating around nerve cells that enhances signal transmission. Optimal cognitive function contributes to overall mental well-being and can positively affect mood, memory, and concentration.
4. Magnesium: Magnesium is a mineral that plays a vital role in numerous biochemical processes in the body, including the regulation of mood and neurotransmitter production. Here are some of the potential benefits of magnesium on mood and neurotransmitter production:
- Regulation of Neurotransmitters: Magnesium is involved in the synthesis, release, and regulation of neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells in the brain. It helps maintain optimal levels of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which are essential for regulating mood and emotions. By supporting neurotransmitter production and balance, magnesium can contribute to a more stable and positive mood.
- Stress Reduction: Magnesium has been found to have stress-reducing effects. It plays a role in regulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which is involved in the body’s stress response. Adequate magnesium levels help modulate the release of stress hormones like cortisol, reducing the physiological and psychological effects of stress. By promoting a more balanced stress response, magnesium can support a calmer and more relaxed mood.
- Mood Stabilization: Magnesium has been linked to mood stabilization and the prevention of mood disorders. Studies have shown that individuals with lower magnesium levels are more prone to symptoms of depression, anxiety, and irritability. Increasing magnesium intake may help alleviate symptoms of mood disorders and promote a more positive and stable mood.
- Enhanced Serotonin Function: Magnesium is involved in the conversion of tryptophan into serotonin, a neurotransmitter known for its role in regulating mood and promoting feelings of well-being. Magnesium is required as a cofactor for the enzyme that catalyzes this conversion process. By supporting serotonin production and function, magnesium can contribute to a more balanced and positive mood.
- Calming Effect: Magnesium has a natural calming effect on the nervous system. It acts as a natural relaxant by blocking the excessive activity of excitatory neurotransmitters like glutamate. This helps reduce overstimulation and promotes a state of relaxation and tranquility, which can positively influence mood and overall mental well-being.
5. Probiotics: The role of probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria, in mood and neurotransmitter production is an emerging area of research. While the understanding is still developing, here are some potential mechanisms through which probiotics may impact mood and neurotransmitters:
- Gut-Brain Axis Communication: The gut and the brain are connected through a bidirectional communication pathway known as the gut-brain axis. Probiotics can influence this communication by modulating the gut microbiota, improving gut barrier function, and regulating the production of various substances in the gut. This can indirectly affect neurotransmitter production and mood regulation.
- Serotonin Production: Probiotics, particularly certain strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, have been found to stimulate the production of serotonin in the gut. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in mood regulation. Increased serotonin production in the gut may result in increased serotonin levels in the brain, potentially improving mood and overall mental well-being.
- Neurotransmitter Metabolism: Probiotics can influence the metabolism of neurotransmitters such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and dopamine. Some strains of probiotics have been shown to enhance GABA production, which has calming and anxiety-reducing effects. By influencing neurotransmitter metabolism, probiotics may have an indirect impact on mood and emotional balance.
- Inflammation Reduction: Chronic inflammation in the body, including in the gut, has been associated with mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. Probiotics can help modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation in the gut, which may positively influence mood. By decreasing inflammation, probiotics may indirectly support neurotransmitter balance and enhance overall mental well-being.
- Stress Response Regulation: Probiotics may have an impact on the body’s stress response system. Studies suggest that certain strains of probiotics can help regulate the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol, and modulate the body’s response to stress. By improving stress resilience, probiotics may contribute to a more balanced mood and emotional well-being.
In conclusion: Supplementing with 5-HTP, SAMe, Magnesium, methylated B12, and probiotics can be important when using psychedelic drugs due to several reasons:
- Serotonin Support: Psychedelic drugs primarily affect the serotonin system in the brain. By supplementing with 5-HTP, a precursor to serotonin, individuals may help replenish serotonin levels depleted during psychedelic use, which can mitigate the potential for a serotonin deficit and contribute to a more balanced mood.
- Mood Stabilization: SAMe, Magnesium, and methylated B12 have demonstrated mood-enhancing properties. Taking these supplements alongside psychedelic drugs may provide additional support to stabilize mood and emotions, potentially reducing the risk of negative or overwhelming experiences associated with psychedelic use.
- Neuroprotection: Psychedelics can induce neuroplasticity, and ensuring proper brain health and function is essential. Supplements like Magnesium and methylated B12 have neuroprotective effects and can support cognitive function. They may help maintain brain health during psychedelic experiences and aid in recovery afterward.
- Nutrient Replenishment: Psychedelic experiences can be physically and mentally demanding. Supplementing with essential nutrients like Magnesium and methylated B12 can help replenish any deficiencies that may arise during or after psychedelic use, supporting overall well-being.
- Gut Health and Integration: Probiotics play a vital role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Since the gut-brain axis influences mood and cognitive function, taking probiotics alongside psychedelic use can support gut health and potentially enhance the integration of the psychedelic experience.
It’s important to note that while these supplements may have potential benefits, individual responses and requirements may vary. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before combining any supplements with psychedelic drug use. They can provide personalized guidance, assess any potential interactions or contraindications with medications, and help determine the appropriate dosages for optimal safety and effectiveness.
Have a question?Schedule a consultation with Dr. Julia Ward now
Fill the form below and a member of our team will reach out to you. Alternatively, during our working hours, click the number below to talk to us now.